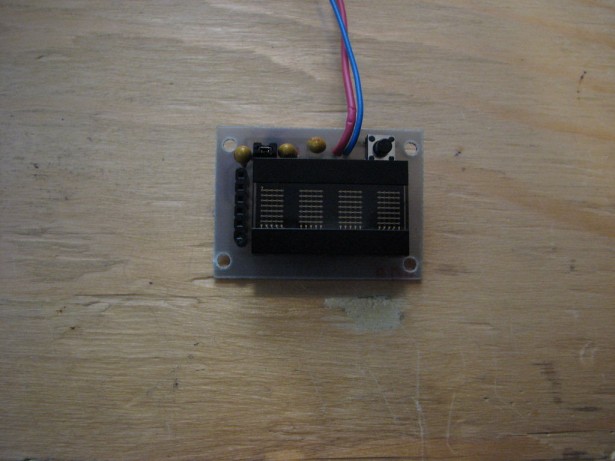
Programmable watch with four character display
Inspired by the Microreader kit, I decided to make a giant watch using similar sixteen segment displays. Twelve hours later, I came out of my masochistic fugue and stopped trying to route a sixteen bit data bus on a single sided pcb small enough to wear on your wrist.
Returning to my digikey box of mystery, I came up with a four character display made up of 5×7 led matrices. 7 bit parallel data input, no need for umpteen current limiting resistors, upper and lower case characters, the rest writes itself.
This instructable is not meant to be a tutorial on creating PCBs or programming PICs. In all fairness, I wouldn’t actually recommend that anyone try to make one of these. If you know enough to follow along, you can probably do a better job than I did. If you don’t know what’s going on, then this instructable isn’t going to teach you all you need to know.
P.S. If you use this to scroll internet catchphrases in public, you are a bad person and should be ashamed.
Step 1: Get your crap together
What you’re going to need:
Comes in red, green, lavender, fuchsia, and maple walnut flavours.
You might be able to get away with another pin-compatible PIC, just make sure to read the datasheet carefully. Either way, you’ll need at least one PIC in the SOIC package and probably a DIP for breadboarding the circuit. The 628A and 648A are identical except for the amount of program memory available (2k vs 4k). Use the 648A unless you have some 628As lying around.
This is a charge pump dc-dc converter. We’re going to use this to make 5V for our display from a 3V coin cell battery. Get a few so that you can destroy at least one.
The passive components are all through hole type. I know the mishmash of surface mount and through hole is kind of aesthetically displeasing but what can you do.
-Capacitors: 10uF (2), 1uF (1)
-Resistors: 10K (1)
-Switch: N/O momentary pushbutton. The clicky kind you see everywhere cheap buttons are needed.
-Pin headers/sockets: Two pins and a jumper, and a single row of 6 sockets. You can substitute pins for the sockets if you enjoy accidentally tearing clothing and skin.
-CR2032 Coin cell and holder.
Supporting cast:
Soldering iron with the pointiest tip you can find. The MCP1253 comes in a surface mount package small enough to be accidentally inhaled.
Copper clad board, etchant, acetone etc for making the PCB.
PIC programmer with an ICSP header and cable.
Some other stuff without which you won’t get very far but that I can’t remember right now.
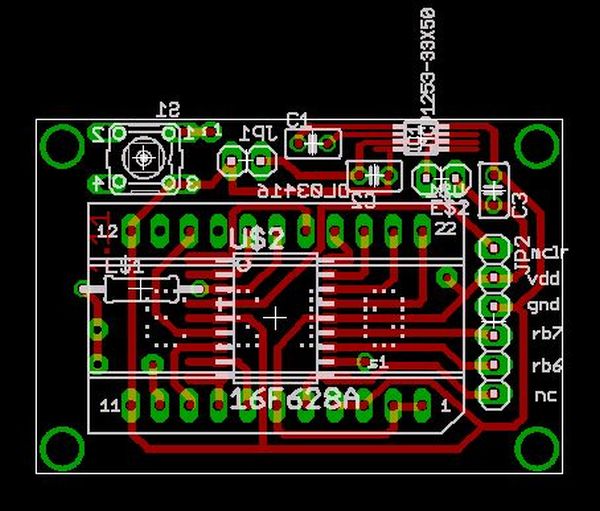
Step 2
PCB fun
The display datasheet lies. It says the cursor select is an active high input. Now since we’re patient and careful, we’ve breadboarded the circuit to discover this before wasting hours making PCBs with CU tied low.
With only one display, we don’t need to worry about addressing. We also don’t care about the cursor function. In fact, I have discovered a truly remarkable list of things we don’t care about, which this instructable is too narrow to contain.
I routed the board freehand for the most part, so I’m not including a pretty Eagle schematic. Mapping PIC outputs to display pins is a lot easier using component footprints. If this is too confusing, get stuf.. I mean I’ll make one up.
I’m not going to go over how to make your own PCB, Instructables is made up of about 50% toner transfer method instructions by my count. Download the Eagle file, print it out 1:1 and mirrored. Iron it onto some copper board for about half an hour, pull the paper off, discover that it didn’t work and repeat about ten times.
If you want to do a nicer jumperless job, have a double sided board made or whatever, the Eagle libaries for the MCP1253 (thanks to someone over at Open Circuits) and the display are attached.
Step 3
Assembly
Some general tips:
1. Start with the MCP1253. This way when you screw it up and smash the board, you aren’t losing a lot.
Tin the traces first, then hold it in place and tack it down. The extra trace length around it should help out, heat the far end and line it up. If you have a steady hand and some fine solder you can do the leads individually. If you bridge any, drag some solder wick across them.
2. After soldering the MSOP, the SOIC PIC will be a walk in the park. Same deal again, tack down the corners then work your way around.
3. Surface mount parts go on the bottom everything else goes on top.