In Part 1 of this series, we have reviewed solar cell performance, how to select and size the supercapacitor, requirements of supercapacitor charging circuits and charging IC characteristics. We will now use two case studies to illustrate these properties in detail.
Case Study 1: Using a small solar cell indoors at low light, 100 lux, to power a Bluetooth low energy sensor using CAP-XX GA109
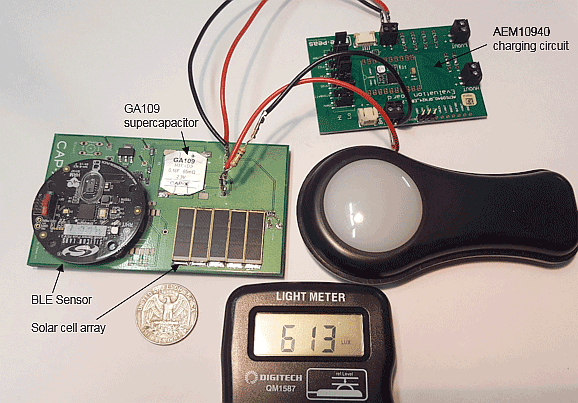
In this case we used a low power BLE sensor operating in low indoor light down to 100 lux. The sensor only operates when there is light, so the supercapacitor only needs to support data acquisition and transmission.
We used a Sensor Puck BLE sensor reporting temperature, relative humidity and light level to a phone app every second. The sensor max-min supply voltage range is 3.0V to 2.0V, therefore we will use a single cell supercapacitor with a maximum cell voltage = 2.5V. Figure 9 shows the current and voltage waveform while the sensor is acquiring and transmitting data. The peak current is ~22mA for 1ms duration, while the sustained burst has an average current of 4.5mA over 12ms, with a small peak of 5mA at the end of the pulse. Figure 5 shows this current is >> solar cell current of 260µA at the peak power point. In this case, we have chosen a CAP-XX GA109 supercapacitor, 180mF, 40mΩ. This is a small prismatic supercapacitor that enables a slender attractive industrial design.
for more detail: Using a supercapacitor for power management and energy storage with a small solar cell, Part 2
