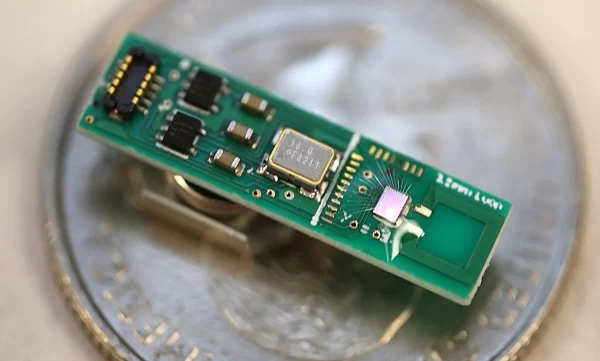
You’re probably swimming in Bluetooth radio signals right now. But none of those are coming from the smallest, lowest-power end of the Internet of Things. These battery-powered and energy-harvesting millimeter-scale sensors are meant to last for years without needing replacement, but their radios can’t muster the energy needed to communicate using even the lowest energy version of Bluetooth, called Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE).
Engineers at the University of Michigan have now built the first millimeter-scale stand-alone device that speaks BLE. Consuming just 0.6 milliwatts during transmission, it would broadcast for 11 years using a typical 5.8-millimeter coin battery. Such a millimeter-scale BLE radio would allow these ant-size sensors to communicate with ordinary equipment, even a smartphone.
The transmitter chip, which debuted last month at IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, had to solve two problems, explains David Wentzloff, the Michigan associate professor who led the research. The first is power consumption, and the second is the size of the antenna. “The size of the antenna is typically physics-based, and you can’t cheat physics,” says Wentzloff. The group’s solution touched on both problems.
An ordinary transmitter circuit requires a tunable RF oscillator to generate the frequency, a power amplifier to boost its amplitude, and an antenna to radiate the signal. The Michigan team combined the oscillator and the antenna in a way that made the amplifier unnecessary. They called their invention a power oscillator.
The key part of an oscillator is the resonant tank circuit: an inductor and a capacitor. Energy sloshes back and forth between the inductor’s magnetic field and the capacitor’s electric field at a resonant frequency determined by the capacitance and inductance. In the new circuit, the team used the antenna itself as the inductor in the resonant tank. Because it was acting as an inductor, the antenna radiated using a changing magnetic field instead of an electric field; that meant it could be more compact.
Read more: TEENY-TINY BLUETOOTH TRANSMITTER RUNS ON LESS THAN 1 MW