A relay is an electromagnetic switch which is used to switch High Voltage/Current using Low power circuits. Relay isolates low power circuits from high power circuits. It is activated by energizing a coil wounded on a soft iron core. The Role and Function of Relays include controlling the flow of electricity between circuits, providing electrical isolation, amplifying signals, and facilitating the automation of various processes. For detailed working of relay please visit this page. A relay should not be directly connected to a microcontroller, it needs a driving circuit.
A relay should not be connected directly to a microcontroller due to following reasons..
- A microcontroller is not able to supply current required for the working of a relay. The maximum current that a PIC Microcontroller can source or sink is 25mA while a relay needs about 50 – 100mA current.
- A relay is activated by energizing its coil. Microcontroller may stop working by the negative voltages produced in the relay due to its back emf.

Interfacing Relay with PIC Microcontroller using Transistor
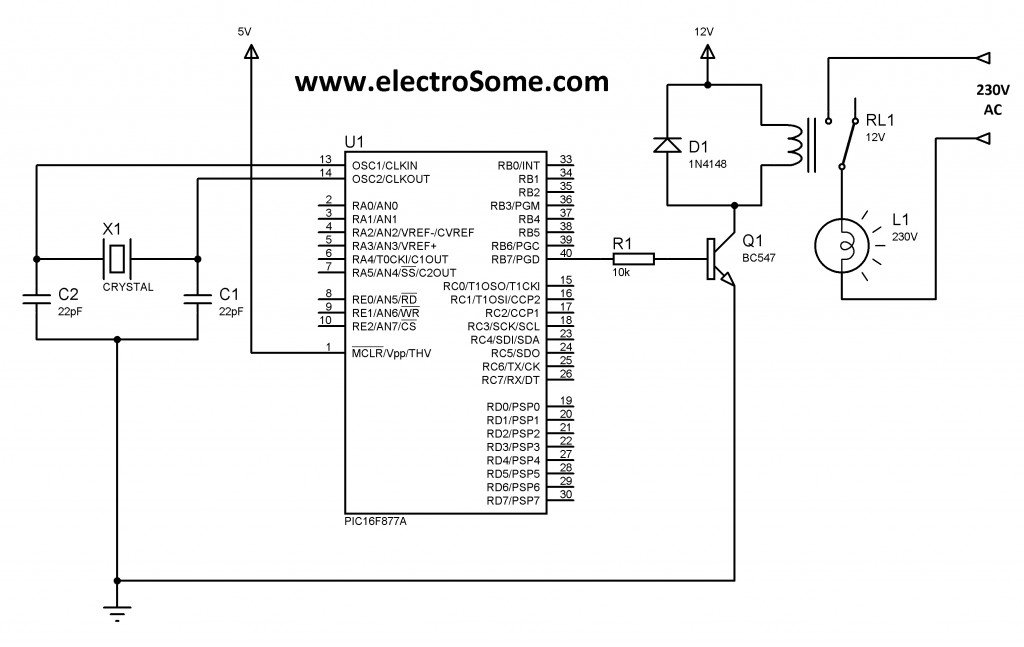
A relay can be easily interfaced with microcontroller using a transistor as shown below. Transistor is wired as a switch which carries the current required for operation of the relay. When the pin RB7 of the PIC microcontroller goes high, the transistor BC547 turns On and current flows through the relay. The diode D1 is used to protect transistor and the microcontroller from Back EMF generated in the relays coil. Normally 1N4148 is preferred as it is a fast switching diode having a peak forward current of 450mA. This diode is also known as freewheeling diode.

Interfacing Relay with PIC using Transistor
Note: VDD and VSS of the pic microcontroller is not shown in the circuit diagram. VDD should be connected to +5V and VSS to GND.
Read More: Interfacing Relay with PIC Microcontroller