Summary of How to configure EUSART in PIC18F4550 Microcontroller
This article explains serial communication using the PIC18F4550 microcontroller's Enhanced USART (EUSART). It covers key communication modes such as asynchronous, synchronous, full-duplex, and half-duplex, and details the configuration of EUSART registers for transmission and reception of data. The article also includes baud rate calculations for different modes, a programming example that echoes received serial data back to a PC via serial port using HyperTerminal, and a hardware setup utilizing the MAX232 level converter for interface between PIC and PC.
Parts used in the Serial Communication using PIC18F4550:
- PIC18F4550 Microcontroller
- MAX232 Level Converter
- PC with Serial Port
- Crystal Oscillator (12 MHz)
- Connection Cables / Wires
Both, Parallel and Serial modes of communication have certain advantages and disadvantages over one another. The serial communication is a preferred option due to its ability of long distance communication with error detection capability. The microcontrollers consist of an inbuilt hardware unit known as USART (Universal Synchronous Asynchronous Reception and Transmission) to facilitate serial transfer of data. For more details, refer to USART in AVR section.
Before starting USART, some general terms related to communication need to be understood. These terms are explained below.
Bit 7 | Bit 6 | Bit 5 | Bit 4 | Bit 3 | Bit 2 | Bit 1 | Bit 0 |
CSRC | TX9 | TXEN | SYNC | SENDB | BRGH | TRMT | TX9D |
Bit 7 | Bit 6 | Bit 5 | Bit 4 | Bit 3 | Bit 2 | Bit 1 | Bit 0 |
SPEN | RX9 | SREN | CREN | ADDEN | FERR | OERR | RX9D |
Fig. 5: Bit configuration of RCSTA /Receive Status and Control Register in EUSART of PIC Microcontroller
Bit 7 | Bit 6 | Bit 5 | Bit 4 | Bit 3 | Bit 2 | Bit 1 | Bit 0 |
SPPIF | ADIF | RCIF | TXIF | SSPIF | CCP1IF | TMR2IF | TMR1IF |
Fig. 6: Bit Configuration of PIR1 /Peripheral Interrupt Request Register of PIC’s EUSART
Bit 7 | Bit 6 | Bit 5 | Bit 4 | Bit 3 | Bit 2 | Bit 1 | Bit 0 |
SPPIE | ADIE | RCIE | TXIE | SSPIE | CCP1IE | TMR2IE | TMR1IE |
Fig. 7: Bit configuration of PIE1/ Peripheral Interrupt Enable Register 1of EUSART in PIC Microcontroller
Bit 7 | Bit 6 | Bit 5 | Bit 4 | Bit 3 | Bit 2 | Bit 1 | Bit 0 |
ABDOVF | RCIDL | RXDTP | TXCKP | BRG16 | — | WUE | ABDEN |
Configuration Bits | BRG/EUSART Mode | Baud Rate Formula | ||
SYNC | BRG16 | BRGH | ||
0 | 0 | 0 | 8-bit/Asynchronous | Fosc / [64 (n + 1)] |
0 | 0 | 1 | 8-bit/Asynchronous | Fosc / [16 (n + 1)] |
0 | 1 | 0 | 16-bit/Asynchronous | |
0 | 1 | 1 | 16-bit/Asynchronous | Fosc / [4 (n + 1)] |
1 | 0 | x | 8-bit/Synchronous | |
1 | 1 | x | 16-bit/Synchronous | |

Project Source Code
###
// Program to depict the configuration of EUSART in PIC18F4550
// This code receives and then transmits the same data back to the PC .. // ..through PC’s Serial Port
// Configuration bits
/* _CPUDIV_OSC1_PLL2_1L, // Divide clock by 2
_FOSC_HS_1H, // Select High Speed (HS) oscillator
_WDT_OFF_2H, // Watchdog Timer off
MCLRE_ON_3H // Master Clear on
*/
void tx_data(unsigned char);
unsigned char rx_data(void);
unsigned char serial_data;
unsigned int i=0;
#define FREQ 12000000 // Frequency = 12MHz
#define baud 9600
#define spbrg_value (((FREQ/64)/baud)-1) // Refer to the formula for Baud rate calculation in Description tab
void main()
{
SPBRG=spbrg_value; // Fill the SPBRG register to set the Baud Rate
RCSTA.SPEN=1; // To activate Serial port (TX and RX pins)
TXSTA.TXEN=1; // To enable transmission
RCSTA.CREN=1; // To enable continuous reception
while(1)
{
serial_data=rx_data(); // Receive data from PC
tx_data(serial_data); // Transmit the same data back to PC
}
}
void tx_data(unsigned char data1)
{
TXREG=data1; // Store data in Transmit register
while(PIR1.TXIF==0); // Wait until TXIF gets low
}
unsigned char rx_data(void)
{
while(PIR1.RCIF==0); // Wait until RCIF gets low
return RCREG; // Retrieve data from reception register
}
###
Circuit Diagrams
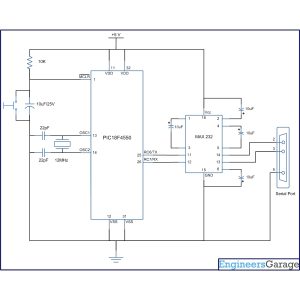
Project Components
Project Video
Source: How to configure EUSART in PIC18F4550 Microcontroller
