In the first part of this discussion, the features of ACS712 device were briefly discussed. Now we will use that theory to implement the ACS712 sensor to make a simple DC current meter. The analog output voltage from the sensor is measured through an ADC channel of the PIC16F1847 microcontroller. A voltage to current conversion equation will be derived and implemented in the firmware of the PIC microcontroller and the actual load current will be displayed on a character LCD.
Experimental circuit setup
We are going to setup a test experiment to demonstrate the use of ACS712 to measure a DC current. I am using an ACS712-05B breakout module (you can find them cheap on ebay) for this purpose.
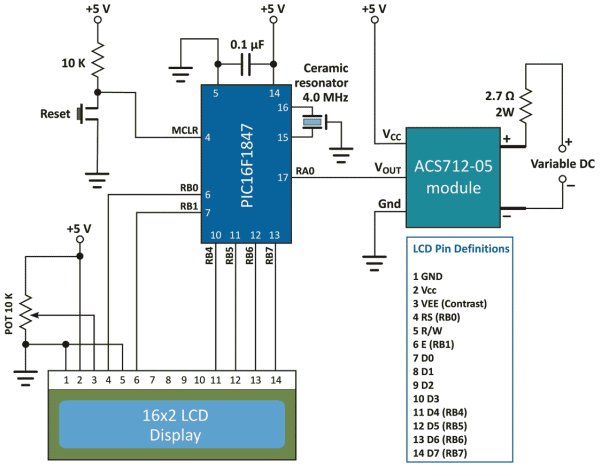
The experimental circuit diagram of the DC current meter is shown below. A 2.7 Ω (rated 2 Watt) resistor is connected in series with the current terminals and a varying dc voltage is applied to vary the current through the resistor and the current path. The output of the sensor module goes to AN0 (pin 17) ADC channel of the PIC16F1847 microcontroller. A 16×2 character LCD is used to display the measured current output.
I am using my PIC16F1847 breadboard module along with the Experimenter’s I/O board to demonstrate this experiment.
The microcontroller uses the supply voltage (+5V) as reference for A/D conversion. The digitized sensor output is processed through software to convert it to the actual current value. The mathematics involved in the process is described in the white board below.
For Vcc=5V and ADC Vref=5V, the relationship between output voltage and ADC Count is
But,
Important note: The calculations shown above considered supply voltage Vcc = Vref = 5.0 V. Interestingly, the final equation relating I and Count remains the same even the power supply fluctuates. For example, suppose Vcc fluctuates and becomes 4.0 V. Then, the sensitivity of the ACS712-05B also changes to 0.185 x 4/5 = 0.148 mV.
The equation clearly tells that the current resolution for this setup is 26.4 mA, which corresponds to count 513, one count higher than the zero current offset. Therefore, this kind of arrangement is not suitable for measuring low current. You need an external Op-Amp circuit to enhance the resolution and be able to make more sensitive current measurement. If you are interested on that, you can visit Sparkfun’s ACS712 Low Current Sensor Breakout page that provides a circuit diagram for such an arrangement.
For more detail: A brief overview of Allegro ACS712 current sensor. Part 2 – Interface the sensor with a PIC microcontroller

