Contents
hide
The Compact Flash Library provides routines for accessing data on Compact Flash card (abbr. CF further in text). CF cards are widely used memory elements, commonly used with digital cameras. Great capacity and excellent access time of only a few microseconds make them very attractive for microcontroller applications.
In CF card, data is divided into sectors. One sector usually comprises 512 bytes. Routines for file handling, the
Cf_Fat routines, are not performed directly but successively through 512B buffer.Important :
- Routines for file handling can be used only with FAT16 file system.
- Library functions create and read files from the root directory only.
- Library functions populate both FAT1 and FAT2 tables when writing to files, but the file data is being read from the FAT1 table only; i.e. there is no recovery if the FAT1 table gets corrupted.
- If MMC/SD card has Master Boot Record (MBR), the library will work with the first available primary (logical) partition that has non-zero size. If MMC/SD card has Volume Boot Record (i.e. there is only one logical partition and no MBRs), the library works with entire card as a single partition. For more information on MBR, physical and logical drives, primary/secondary partitions and partition tables, please consult other resources, e.g. Wikipedia and similar.
- Before writing operation, make sure not to overwrite boot or FAT sector as it could make your card on PC or digital camera unreadable. Drive mapping tools, such as Winhex, can be of great assistance.

External dependencies of Compact Flash Library
| The following variables must be defined in all projects using Compact Flash Library: | Description : | Example : |
|---|---|---|
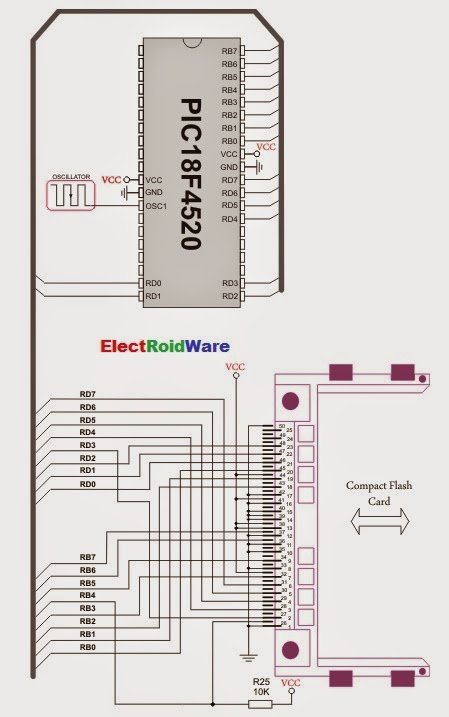
extern sfr char CF_Data_Port; | Compact Flash Data Port. | char CF_Data_Port at PORTD; |
extern sfr sbit CF_RDY; | Ready signal line. | sbit CF_RDY at RB7_bit; |
extern sfr sbit CF_WE; | Write Enable signal line. | sbit CF_WE at LATB6_bit; |
extern sfr sbit CF_OE; | Output Enable signal line. | sbit CF_OE at LATB5_bit; |
extern sfr sbit CF_CD1; | Chip Detect signal line. | sbit CF_CD1 at RB4_bit; |
extern sfr sbit CF_CE1; | Chip Enable signal line. | sbit CF_CE1 at LATB3_bit; |
extern sfr sbit CF_A2; | Address pin 2. | sbit CF_A2 at LATB2_bit; |
extern sfr sbit CF_A1; | Address pin 1. | sbit CF_A1 at LATB1_bit; |
extern sfr sbit CF_A0; | Address pin 0. | sbit CF_A0 at LATB0_bit; |
extern sfr sbit CF_RDY_direction; | Direction of the Ready pin. | sbit CF_RDY_direction at TRISB7_bit; |
extern sfr sbit CF_WE_direction; | Direction of the Write Enable pin. | sbit CF_WE_direction at TRISB6_bit; |
extern sfr sbit CF_OE_direction; | Direction of the Output Enable pin. | sbit CF_OE_direction at TRISB5_bit; |
extern sfr sbit CF_CD1_direction; | Direction of the Chip Detect pin. | sbit CF_CD1_direction at TRISB4_bit; |
extern sfr sbit CF_CE1_direction; | Direction of the Chip Enable pin. | sbit CF_CE1_direction at TRISB3_bit; |
extern sfr sbit CF_A2_direction; | Direction of the Address 2 pin. | sbit CF_A2_direction at TRISB2_bit; |
extern sfr sbit CF_A1_direction; | Direction of the Address 1 pin. | sbit CF_A1_direction at TRISB1_bit; |
extern sfr sbit CF_A0_direction; | Direction of the Address 0 pin. | sbit CF_A0_direction at TRISB0_bit; |
Library Routines
- Cf_Init
- Cf_Detect
- Cf_Enable
- Cf_Disable
- Cf_Read_Init
- Cf_Read_Byte
- Cf_Write_Init
- Cf_Write_Byte
- Cf_Read_Sector
- Cf_Write_Sector
Routines for file handling:
- Cf_Fat_Init
- Cf_Fat_QuickFormat
- Cf_Fat_Assign
- Cf_Fat_Reset
- Cf_Fat_Read
- Cf_Fat_Rewrite
- Cf_Fat_Append
- Cf_Fat_Delete
- Cf_Fat_Write
- Cf_Fat_Set_File_Date
- Cf_Fat_Get_File_Date
- Cf_Fat_Get_File_Date_Modified
- Cf_Fat_Get_File_Size
- Cf_Fat_Get_Swap_File
The following routine is for the internal use by compiler only:
- Cf_Issue_ID_Command
Cf_Init
| Prototype | void Cf_Init(); |
|---|---|
| Returns | Nothing. |
| Description | Initializes ports appropriately for communication with CF card. |
| Requires | Global variables :
must be defined before using this function. |
| Example | // set compact flash pinout char Cf_Data_Port at PORTD; sbit CF_RDY at RB7_bit; sbit CF_WE at LATB6_bit; // for writing to output pin always use latch (PIC18 family) sbit CF_OE at LATB5_bit; // for writing to output pin always use latch (PIC18 family) sbit CF_CD1 at RB4_bit; sbit CF_CE1 at LATB3_bit; // for writing to output pin always use latch (PIC18 family) sbit CF_A2 at LATB2_bit; // for writing to output pin always use latch (PIC18 family) sbit CF_A1 at LATB1_bit; // for writing to output pin always use latch (PIC18 family) sbit CF_A0 at LATB0_bit; // for writing to output pin always use latch (PIC18 family) sbit CF_RDY_direction at TRISB7_bit; sbit CF_WE_direction at TRISB6_bit; sbit CF_OE_direction at TRISB5_bit; sbit CF_CD1_direction at TRISB4_bit; sbit CF_CE1_direction at TRISB3_bit; sbit CF_A2_direction at TRISB2_bit; sbit CF_A1_direction at TRISB1_bit; sbit CF_A0_direction at TRISB0_bit; // end of cf pinout ... Cf_Init(); // initialize CF |
Cf_Detect
| Prototype | unsigned short Cf_Detect(void); |
|---|---|
| Returns |
|
| Description | Checks for presence of CF card by reading the chip detect pin. |
| Requires | The corresponding MCU ports must be appropriately initialized for CF card. |
| Example | // Wait until CF card is inserted: do asm nop; while (!Cf_Detect()); |
Cf_Enable
| Prototype | void Cf_Enable(void); |
|---|---|
| Returns | Nothing. |
| Description | Enables the device. Routine needs to be called only if you have disabled the device by means of the Cf_Disable routine. These two routines in conjunction allow you to free/occupy data line when working with multiple devices. |
| Requires | The corresponding MCU ports must be appropriately initialized for CF card. |
| Example | // enable compact flash Cf_Enable(); |
Cf_Disable
| Prototype | void Cf_Disable(void); |
|---|---|
| Returns | Nothing. |
| Description | Routine disables the device and frees the data lines for other devices. To enable the device again, call Cf_Enable. These two routines in conjunction allow you to free/occupy data line when working with multiple devices. |
| Requires | The corresponding MCU ports must be appropriately initialized for CF card. |
| Example | // disable compact flash Cf_Disable(); |
Cf_Read_Init
| Prototype | void Cf_Read_Init(unsigned long address, unsigned short sector_count); |
|---|---|
| Returns | Nothing. |
| Description | Initializes CF card for reading. Parameters :
|
| Requires | The corresponding MCU ports must be appropriately initialized for CF card. |
| Example | // initialize compact flash for reading from sector 590 Cf_Read_Init(590, 1); |
Cf_Read_Byte
| Prototype | unsigned short Cf_Read_Byte(void); |
|---|---|
| Returns | Returns a byte read from Compact Flash sector buffer. Note : Higher byte of the Note : Higher byte of the unsigned return value is cleared. |
| Description | Reads one byte from Compact Flash sector buffer location currently pointed to by internal read pointers. These pointers will be autoicremented upon reading. |
| Requires | The corresponding MCU ports must be appropriately initialized for CF card. CF card must be initialized for reading operation. |
| Example | // Read a byte from compact flash: char data; ... data = Cf_Read_Byte(); |
Cf_Write_Init
| Prototype | void Cf_Write_Init(unsigned long address, unsigned short sectcnt); |
|---|---|
| Returns | Nothing. |
| Description | Initializes CF card for writing. Parameters :
|
| Requires | The corresponding MCU ports must be appropriately initialized for CF card. |
| Example | // initialize compact flash for writing to sector 590 Cf_Write_Init(590, 1); |
Cf_Write_Byte
| Prototype | void Cf_Write_Byte(unsigned short data_); |
|---|---|
| Returns | Nothing. |
| Description | Writes a byte to Compact Flash sector buffer location currently pointed to by writing pointers. These pointers will be autoicremented upon reading. When sector buffer is full, its contents will be transfered to appropriate flash memory sector. Parameters :
|
| Requires | The corresponding MCU ports must be appropriately initialized for CF card. CF card must be initialized for writing operation. |
| Example | char data_ = 0xAA; ... Cf_Write_Byte(data_); |
Cf_Read_Sector
| Prototype | void Cf_Read_Sector(unsigned long sector_number, unsigned short *buffer); |
|---|---|
| Returns | Nothing. |
| Description | Reads one sector (512 bytes). Read data is stored into buffer provided by the buffer parameter.Parameters :
|
| Requires | The corresponding MCU ports must be appropriately initialized for CF card. |
| Example | // read sector 22 unsigned short data[512]; ... Cf_Read_Sector(22, data); |
Cf_Write_Sector
| Prototype | void Cf_Write_Sector(unsigned long sector_number, unsigned short *buffer); |
|---|---|
| Returns | Nothing. |
| Description | Writes 512 bytes of data provided by the buffer parameter to one CF sector.Parameters :
|
| Requires | The corresponding MCU ports must be appropriately initialized for CF card. |
| Example | // write to sector 22 unsigned short data[512]; ... Cf_Write_Sector(22, data); |
Cf_Fat_Init
| Prototype | unsigned short Cf_Fat_Init(); |
|---|---|
| Returns |
|
| Description | Initializes CF card, reads CF FAT16 boot sector and extracts necessary data needed by the library. |
| Requires | Nothing. |
| Example | // Init the FAT library
if (!Cf_Fat_Init()) { // Init the FAT library
...
}
|
Cf_Fat_QuickFormat
| Prototype | unsigned char Cf_Fat_QuickFormat(char *cf_fat_label); |
|---|---|
| Returns |
|
| Description | Formats to FAT16 and initializes CF card. Parameters :
|
| Requires | Nothing. |
| Example | //--- format and initialize the FAT library -
if (!Cf_Fat_QuickFormat(&cf_fat_label)) {
...
}
|
Cf_Fat_Assign
| Prototype | unsigned short Cf_Fat_Assign(char *filename, char file_cre_attr); | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Returns |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Assigns file for file operations (read, write, delete…). All subsequent file operations will be applied over the assigned file. Parameters :
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Requires | CF card and CF library must be initialized for file operations. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Example | // create file with archive attributes if it does not already exist
Cf_Fat_Assign("MIKRO007.TXT",0xA0); |
Cf_Fat_Reset
| Prototype | void Cf_Fat_Reset(unsigned long *size); |
|---|---|
| Returns | Nothing. |
| Description | Opens currently assigned file for reading. Parameters :
|
| Requires | CF card and CF library must be initialized for file operations. File must be previously assigned. |
| Example | unsigned long size; ... Cf_Fat_Reset(size); |
Cf_Fat_Read
| Prototype | void Cf_Fat_Read(unsigned short *bdata); |
|---|---|
| Returns | Nothing. |
| Description | Reads a byte from currently assigned file opened for reading. Upon function execution file pointers will be set to the next character in the file. Parameters :
|
| Requires | CF card and CF library must be initialized for file operations. File must be previously assigned. File must be open for reading. |
| Example | char character; ... Cf_Fat_Read(&character); |
Cf_Fat_Rewrite
| Prototype | void Cf_Fat_Rewrite(); |
|---|---|
| Returns | Nothing. |
| Description | Opens currently assigned file for writing. If the file is not empty its content will be erased. |
| Requires | CF card and CF library must be initialized for file operations. The file must be previously assigned. |
| Example | // open file for writing Cf_Fat_Rewrite(); |
Cf_Fat_Append
| Prototype | void Cf_Fat_Append(); |
|---|---|
| Returns | Nothing. |
| Description | Opens currently assigned file for appending. Upon this function execution file pointers will be positioned after the last byte in the file, so any subsequent file writing operation will start from there. |
| Requires | CF card and CF library must be initialized for file operations. File must be previously assigned. |
| Example | // open file for appending Cf_Fat_Append(); |
 Cf_Fat_Delete
Cf_Fat_Delete
| Prototype | void Cf_Fat_Delete(); |
|---|---|
| Returns | Nothing. |
| Description | Deletes currently assigned file from CF card. |
| Requires | CF card and CF library must be initialized for file operations. File must be previously assigned. |
| Example | // delete current file Cf_Fat_Delete(); |
Cf_Fat_Write
| Prototype | void Cf_Fat_Write(char *fdata, unsigned data_len); |
|---|---|
| Returns | Nothing. |
| Description | Writes requested number of bytes to currently assigned file opened for writing. Parameters :
|
| Requires | CF card and CF library must be initialized for file operations. File must be previously assigned. File must be open for writing. |
| Example | char file_contents[42]; ... Cf_Fat_Write(file_contents, 42); // write data to the assigned file |
Cf_Fat_Set_File_Date
| Prototype | void Cf_Fat_Set_File_Date(unsigned int year, unsigned short month, unsigned short day, unsigned short hours, unsigned short mins, unsigned short seconds); |
|---|---|
| Returns | Nothing. |
| Description | Sets the date/time stamp. Any subsequent file writing operation will write this stamp to currently assigned file’s time/date attributs. Parameters :
|
| Requires | CF card and CF library must be initialized for file operations. File must be previously assigned. File must be open for writing. |
For more detail: Connect Flash Card with PIC18F4520