This post provides the code for interfacing 24LC64 EEPROM with PIC12F675 microcontroller. This 24LC64 EEPROM has i2c based interface and PIC12F675 doesn’t have any built in i2c modules, so software i2c module is created in the code. This code is written in C language using MPLAB with HI-TECH C compiler. You can download this code from the ‘Downloads‘ section at the bottom of this page.
It is assumed that you know how to interface LCD with PIC12F675 microcontroller. If you don’t then please read this page first, before proceeding with this article. It is also assumed that you know how to create software i2c module in PIC12F675, if you don’t then please read this page first. You should also read how to write/read a byte in/from 24LC64 EEPROM from it’s datasheet.
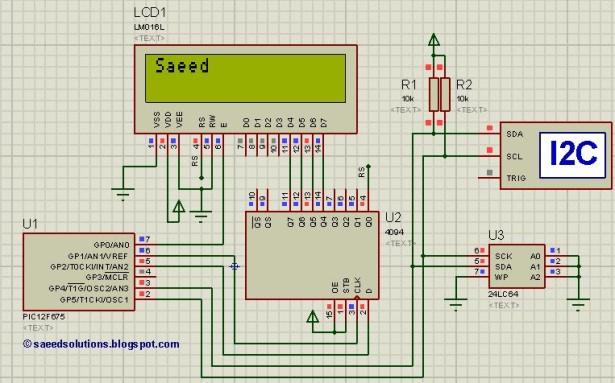
The result of simulating the code in Proteus is shown below.
In the above circuit[1], GP4 pin is being used as SDA pin and GP5 pin is the SCK pin. Both of these pins are pulled up using 10K resistors as required for i2c protocol. 24LC64 EEPROM is the slave device, while PIC12F675 is configured to be the master. LCD is also attached with PIC12F675, just to show the values received from the EEPROM, otherwise it is not required in this circuit. Proteus provides an ‘I2C Debugger Tool‘ which is attached on the SDA and SCK pins in the above circuit, this debugger shows all the activity on i2c bus[2]. It is attached in the circuit just for debugging purposes.
In the code, string ‘Saeed’ is stored in the 24LC64 EEPROM and then retrieved back and displayed on the LCD. As shown in Figure 1, ‘Saeed‘ is correctly displayed on the LCD, this shows that it was stored and retrieved from 24LC64 EEPROM successfully.
Code
The code for the main function is shown below.
In the main function, firstly ADC and comparator are turned off to make pins digital IO pins instead of analog pins using InitCCT() function. Then LCD is initialized using InitLCD() function. Then i2c pins are initialized using InitI2C() function. Then Write_Byte_To_24LC64_EEPROM(0x0001, ‘d’); function writes 0x64 (i-e ‘d’) value on 0x0001 address in the EEPROM. After that, Read_Byte_From_24LC64_EEPROM(0x0001); function reads a single byte from 0x0001 address and saves this value in RxByte variable.
Write_Page_To_24LC64_EEPROM(0x0020, TxArray, 4); function writes 4 bytes present in the TxArray starting from address 0x0020. And Read_Bytes_From_24LC64_EEPROM(0x0020, RxArray, 4); function reads 4 bytes from the starting address of 0x0020 and saves these bytes in RxArray. In the end all of these 5 received bytes are displayed on the LCD. You can verify from Figure 1, that all of these bytes were correctly received and displayed on the LCD. Using these simple read and write functions you can easily interface 24LC64 EEPROM with PIC12F675.
Downloads
24LC64 EEPROM interfacing with PIC12F675 code was compiled in MPLAB v8.85 with HI-TECH C v9.83 compiler and simulation was made in Proteus v7.10. To download code and Proteus simulation click here.
For more detail: Interfacing of PIC12F675 with (i2c based) 24LC64 EEPROM (code and Proteus simulation)