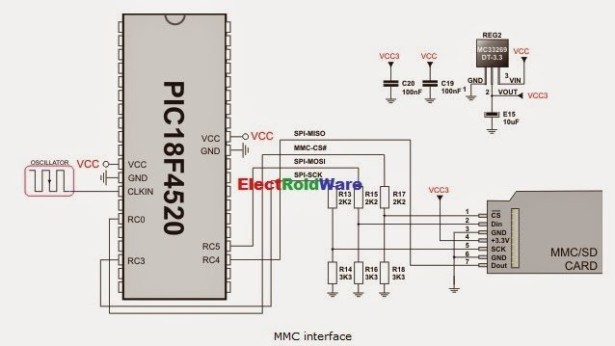
The Multi Media Card (MMC) is a Flash memory card standard. MMC cards are currently available in sizes up to and including 32 GB and are used in cellular phones, digital audio players, digital cameras and PDA’s.
mikroC PRO for PIC provides a library for accessing data on Multi Media Card via SPI communication. This library also supports SD (Secure Digital) and high capacity SDHC (Secure Digital High Capacity) memory cards .
Secure Digital Card
Secure Digital (SD) is a Flash memory card standard, based on the older Multi Media Card (MMC) format.
SD cards are currently available in sizes of up to and including 2 GB, and are used in digital cameras, digital camcorders, handheld computers, media players, mobile phones, GPS receivers, video games and PDAs.
Secure Digital High Capacity Card
SDHC (Secure Digital High Capacity, SD 2.0) is an extension of the SD standard which increases card’s storage capacity up to 32 GB by using sector addressing instead of byte addressing in the previous SD standard.
SDHC cards share the same physical and electrical form factor as older (SD 1.x) cards, allowing SDHC-devices to support both newer SDHC cards and older SD-cards. The current standard limits the maximum capacity of an SDHC card to 32 GB.
- Routines for file handling can be used only with FAT16 file system.
- Library functions create and read files from the root directory only.
- Library functions populate both FAT1 and FAT2 tables when writing to files, but the file data is being read from the FAT1 table only; i.e. there is no recovery if the FAT1 table gets corrupted.
- If MMC/SD card has Master Boot Record (MBR), the library will work with the first available primary (logical) partition that has non-zero size. If MMC/SD card has Volume Boot Record (i.e. there is only one logical partition and no MBRs), the library works with entire card as a single partition. For more information on MBR, physical and logical drives, primary/secondary partitions and partition tables, please consult other resources, e.g. Wikipedia and similar.
- Before write operation, make sure you don’t overwrite boot or FAT sector as it could make your card on PC or digital camera unreadable. Drive mapping tools, such as Winhex, can be of a great assistance.
- Library uses SPI module for communication. The user must initialize the appropriate SPI module before using the MMC Library.
- For MCUs with multiple SPI modules it is possible to initialize all of them and then switch by using the
SPI_Set_Active()function. See the SPI Library functions. - MMC FAT 16 Library works with PIC18 family only.
The SPI module has to be initialized through SPIx_Init_Advanced routine with the following parameters:
- SPI Master
- Primary prescaler 64
- Data sampled in the middle of data output time
- Clock idle low
- Serial output data changes on transition form low to high edge
External dependencies of MMC Library
| The following variable must be defined in all projects using MMC library: | Description : | Example : |
|---|---|---|
extern sfr sbit Mmc_Chip_Select; |
Chip select pin. | sbit Mmc_Chip_Select at RC0_bit; |
extern sfr sbit Mmc_Chip_Select_Direction; |
Direction of the chip select pin. | sbit Mmc_Chip_Select_Direction at TRISC0_bit; |
Library Routines
- Mmc_Init
- Mmc_Read_Sector
- Mmc_Write_Sector
- Mmc_Read_Cid
- Mmc_Read_Csd
- Mmc_Multi_Read_Start
- Mmc_Multi_Read_Sector
- Mmc_Multi_Read_Stop
Routines for file handling:
- Mmc_Fat_Init
- Mmc_Fat_QuickFormat
- Mmc_Fat_Assign
- Mmc_Fat_Reset
- Mmc_Fat_Read
- Mmc_Fat_Rewrite
- Mmc_Fat_Append
- Mmc_Fat_Delete
- Mmc_Fat_Write
- Mmc_Fat_Set_File_Date
- Mmc_Fat_Get_File_Date
- Mmc_Fat_Get_File_Date_Modified
- Mmc_Fat_Get_File_Size
- Mmc_Get_File_Write_Sector
- Mmc_Fat_Get_Swap_File
- Mmc_Fat_Tell
- Mmc_Fat_Seek
- Mmc_Fat_Rename
- Mmc_Fat_MakeDir
- Mmc_Fat_RenameDir
- Mmc_Fat_RemoveDir
- Mmc_Fat_ChangeDir
- Mmc_Fat_Exists
- Mmc_Fat_Dir
- Mmc_Fat_ReadDir
- Mmc_Fat_Activate
- Mmc_Fat_ReadN
- Mmc_Fat_Open
- Mmc_Fat_Close
- Mmc_Fat_EOF
Mmc_Init
| Prototype | unsigned char Mmc_Init(); |
|---|---|
| Returns |
|
| Description | Initializes MMC through hardware SPI interface. Mmc_Init needs to be called before using other functions of this library. |
| Requires | The appropriate hardware SPI module must be previously initialized. Global variables :
must be defined before using this function. The appropriate hardware SPI module must be previously initialized. See the SPI1_Init, SPI1_Init_Advanced routines. |
| Example |
// MMC module connections sfr sbit Mmc_Chip_Select at RC0_bit; sfr sbit Mmc_Chip_Select_Direction at TRISC0_bit; // MMC module connections ... SPI1_Init(); error = Mmc_Init(); // Init with CS line at RC0_bit |
Mmc_Read_Sector
| Prototype | unsigned char Mmc_Read_Sector(unsigned long sector, char *dbuff); |
|---|---|
| Returns |
|
| Description | The function reads one sector (512 bytes) from MMC card. Parameters:
|
| Requires | MMC/SD card must be initialized. |
| Example |
// read sector 510 of the MMC/SD card unsigned int error; unsigned long sectorNo = 510; char dataBuffer[512]; ... error = Mmc_Read_Sector(sectorNo, dataBuffer); |
Mmc_Write_Sector
| Prototype | unsigned char Mmc_Write_Sector(unsigned long sector, char *dbuff); |
|---|---|
| Returns |
|
| Description | The function writes 512 bytes of data to one MMC card sector. Parameters:
|
| Requires | MMC/SD card must be initialized. |
| Example |
// write to sector 510 of the MMC/SD card unsigned int error; unsigned long sectorNo = 510; char dataBuffer[512]; ... error = Mmc_Write_Sector(sectorNo, dataBuffer); |
Mmc_Read_Cid
| Prototype | unsigned char Mmc_Read_Cid(char *data_cid); |
|---|---|
| Returns |
|
| Description | The function reads 16-byte CID register. Parameters:
|
| Requires | MMC/SD card must be initialized. |
| Example |
unsigned int error; char dataBuffer[16]; ... error = Mmc_Read_Cid(dataBuffer); |
Mmc_Read_Csd
| Prototype | unsigned char Mmc_Read_Csd(char *data_csd); |
|---|---|
| Returns |
|
| Description | The function reads 16-byte CSD register. Parameters:
|
| Requires | MMC/SD card must be initialized. |
| Example |
unsigned int error; char dataBuffer[16]; ... error = Mmc_Read_Csd(dataBuffer); |
Mmc_Multi_Read_Start
| Prototype | unsigned int Mmc_Multi_Read_Start(unsigned long sector); |
|---|---|
| Description | The function starts multi read mode, sectors are sequentially read starting from the sector given in the function argument. |
| Parameters |
|
| Returns |
|
| Requires | MMC/SD card must be initialized. |
| Example |
unsigned int error; char sector; ... error = Mmc_Multi_Read_Start(sector); |
| Notes | None. |
Mmc_Multi_Read_Sector
| Prototype | void Mmc_Multi_Read_Sector(char *dbuff); |
|---|---|
| Description | The function reads sectors in multi read mode and places them in the buffer given as the function argument. Next function call reads the subsequent sector. Buffer size should be 512B. |
| Parameters |
|
| Returns | Nothing. |
| Requires | MMC/SD card must be initialized. |
| Example |
unsigned int error; ... Mmc_Multi_Read_Sector(buffer); |
| Notes | None. |
Mmc_Multi_Read_Stop
| Prototype | unsigned int Mmc_Multi_Read_Stop(); |
|---|---|
| Description | The function stops multi read mode sequence. |
| Parameters | None. |
| Returns |
|
| Requires | MMC/SD card must be initialized. |
| Example |
Mmc_Multi_Read_Stop; |
| Notes | None. |
Mmc_Fat_Init
| Prototype | unsigned short Mmc_Fat_Init(); |
|---|---|
| Returns |
|
| Description | Initializes MMC/SD card, reads MMC/SD FAT16 boot sector and extracts necessary data needed by the library.
Note : MMC/SD card has to be formatted to FAT16 file system.
|
| Requires | Global variables :
must be defined before using this function. The appropriate hardware SPI module must be previously initialized. |
| Example |
// MMC module connections
sfr sbit Mmc_Chip_Select at RC0_bit;
sfr sbit Mmc_Chip_Select_Direction at TRISC0_bit;
// MMC module connections
// Initialize SPI1 module
SPI1_Init_Advanced(_SPI_MASTER_OSC_DIV64, _SPI_DATA_SAMPLE_MIDDLE,_SPI_CLK_IDLE_LOW, _SPI_LOW_2_HIGH);
// use fat16 quick format instead of init routine if a formatting is needed
if (!Mmc_Fat_Init()) {
// reinitialize SPI1 at higher speed
SPI1_Init_Advanced(_SPI_MASTER_OSC_DIV4, _SPI_DATA_SAMPLE_MIDDLE, _SPI_CLK_IDLE_LOW, _SPI_LOW_2_HIGH);
...
}
|
Mmc_Fat_QuickFormat
| Prototype | unsigned char Mmc_Fat_QuickFormat(char *mmc_fat_label); |
|---|---|
| Returns |
|
| Description | Formats to FAT16 and initializes MMC/SD card. Parameters:
Note :
|
| Requires | The appropriate hardware SPI module must be previously initialized. |
| Example |
// Format and initialize MMC/SD card and MMC_FAT16 library globals
if (!Mmc_Fat_QuickFormat(&mmc_fat_label)) {
...
}
|
Mmc_Fat_Assign
| Prototype | unsigned short Mmc_Fat_Assign(char *filename, char file_cre_attr); | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Returns |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Assigns file for file operations (read, write, delete…). All subsequent file operations will be applied on an assigned file. Parameters:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Requires | MMC/SD card and MMC library must be initialized for file operations. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Example |
// create file with archive attribute if it does not already exist
Mmc_Fat_Assign("MIKRO007.TXT",0xA0);
|
Mmc_Fat_Reset
| Prototype | void Mmc_Fat_Reset(unsigned long *size); |
|---|---|
| Returns | Nothing. |
| Description | Procedure resets the file pointer (moves it to the start of the file) of the assigned file, so that the file can be read. Parameters:
|
| Requires | MMC/SD card and MMC library must be initialized for file operations. The file must be previously assigned. |
| Example |
unsigned long size; ... Mmc_Fat_Reset(&size); |
Mmc_Fat_Read
| Prototype | void Mmc_Fat_Read(unsigned short *bdata); |
|---|---|
| Returns | Nothing. |
| Description | Reads a byte from the currently assigned file opened for reading. Upon function execution, file pointers will be set to the next character in the file. Parameters:
|
| Requires | MMC/SD card and MMC library must be initialized for file operations. The file must be previously assigned. The file must be opened for reading. |
| Example |
char character; ... Mmc_Fat_Read(&character); |
Mmc_Fat_Rewrite
| Prototype | void Mmc_Fat_Rewrite(); |
|---|---|
| Returns | Nothing. |
| Description | Opens the currently assigned file for writing. If the file is not empty its content will be erased. |
| Requires | MMC/SD card and MMC library must be initialized for file operations. The file must be previously assigned. |
| Example |
// open file for writing Mmc_Fat_Rewrite(); |
Mmc_Fat_Append
| Prototype | void Mmc_Fat_Append(); |
|---|---|
| Returns | Nothing. |
| Description | Opens the currently assigned file for appending. Upon this function execution file pointers will be positioned after the last byte in the file, so any subsequent file write operation will start from there. |
| Requires | MMC/SD card and MMC library must be initialized for file operations. The file must be previously assigned. |
| Example |
// open file for appending Mmc_Fat_Append(); |
Mmc_Fat_Delete
| Prototype | char Mmc_Fat_Delete(); |
|---|---|
| Returns |
|
| Description | Deletes currently assigned file from MMC/SD card. |
| Requires | MMC/SD card and MMC library must be initialized for file operations. The file must be previously assigned. |
| Example |
// delete current file if (Mmc_Fat_Delete() == 0) ... |
Mmc_Fat_Write
| Prototype | void Mmc_Fat_Write(char *fdata, unsigned data_len); |
|---|---|
| Returns | Nothing. |
| Description | Writes requested number of bytes to the currently assigned file opened for writing. Parameters:
|
| Requires | MMC/SD card and MMC library must be initialized for file operations. The file must be previously assigned. The file must be opened for writing. |
| Example |
Mmc_Fat_Write(txt,255);
Mmc_Fat_Write("Hello world",255);
|
Mmc_Fat_Set_File_Date
| Prototype | void Mmc_Fat_Set_File_Date(unsigned int year, unsigned short month, unsigned short day, unsigned short hours, unsigned short mins, unsigned short seconds); |
|---|---|
| Returns | Nothing. |
| Description | Sets the date/time stamp. Any subsequent file write operation will write this stamp to the currently assigned file’s time/date attributs. Parameters:
|
| Requires | MMC/SD card and MMC library must be initialized for file operations. The file must be previously assigned. The file must be opened for writing. |
| Example |
// April 1st 2005, 18:07:00 Mmc_Fat_Set_File_Date(2005, 4, 1, 18, 7, 0); |
Mmc_Fat_Get_File_Date
| Prototype | void Mmc_Fat_Get_File_Date(unsigned int *year, unsigned short *month, unsigned short *day, unsigned short *hours, unsigned short *mins); |
|---|---|
| Returns | Nothing. |
| Description | Reads time/date attributes of the currently assigned file. Parameters:
|
| Requires | MMC/SD card and MMC library must be initialized for file operations. The file must be previously assigned. |
| Example |
// get Date/time of file unsigned yr; char mnth, dat, hrs, mins; ... file_Name = "MYFILEABTXT"; Mmc_Fat_Assign(file_Name); Mmc_Fat_Get_File_Date(&yr, &mnth, &day, &hrs, &mins); |
Mmc_Fat_Get_File_Date_Modified
| Prototype | void Mmc_Fat_Get_File_Date_Modified(unsigned int *year, unsigned short *month, unsigned short *day, unsigned short *hours, unsigned short *mins); |
|---|---|
| Returns | Nothing. |
| Description | Retrieves the last modification date/time for the currently selected file. Parameters:
|
| Requires | MMC/SD card and MMC library must be initialized for file operations. The file must be previously assigned. |
| Example |
// get modification Date/time of file unsigned yr; char mnth, dat, hrs, mins; ... file_Name = "MYFILEABTXT"; Mmc_Fat_Assign(file_Name); Mmc_Fat_Get_File_Date_Modified(&yr, &mnth, &day, &hrs, &mins); |
Mmc_Fat_Get_File_Size
| Prototype | unsigned long Mmc_Fat_Get_File_Size(); |
|---|---|
| Returns | This function returns size of active file (in bytes). |
| Description | This function reads size of the currently assigned file in bytes. |
| Requires | MMC/SD card and MMC library must be initialized for file operations. The file must be previously assigned. |
| Example |
// get Date/time of file unsigned yr; char mnth, dat, hrs, mins; ... file_name = "MYFILEXXTXT"; Mmc_Fat_Assign(file_name); mmc_size = Mmc_Fat_Get_File_Size; |
Mmc_Get_File_Write_Sector
| Prototype | unsigned long Mmc_Get_File_Write_Sector(); |
|---|---|
| Description | This function returns the current file write sector. |
| Parameters | None. |
| Returns | This function returns the current file write sector. |
| Requires | MMC/SD card and MMC library must be initialized for file operations. The file must be previously assigned. |
| Example |
unsigned long sector; ... sector = Mmc_Get_File_Write_Sector(); |
| Notes | None. |
 Mmc_Fat_Get_Swap_File
Mmc_Fat_Get_Swap_File
| Prototype | unsigned long Mmc_Fat_Get_Swap_File(unsigned long sectors_cnt, char* filename, char file_attr); | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Returns |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | This function is used to create a swap file of predefined name and size on the MMC/SD media. If a file with specified name already exists on the media, search for consecutive sectors will ignore sectors occupied by this file. Therefore, it is recommended to erase such file if it already exists before calling this function. If it is not erased and there is still enough space for a new swap file, this function will delete it after allocating new memory space for a new swap file. The purpose of the swap file is to make reading and writing to MMC/SD media as fast as possible, by using the Mmc_Read_Sector() and Mmc_Write_Sector() functions directly, without potentially damaging the FAT system. The swap file can be considered as a “window” on the media where the user can freely write/read data. Its main purpose in the library is to be used for fast data acquisition; when the time-critical acquisition has finished, the data can be re-written into a “normal” file, and formatted in the most suitable way. Parameters:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Requires | MMC/SD card and MMC library must be initialized for file operations. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Example |
//-------------- Tries to create a swap file, whose size will be at least 100 sectors.
//If it succeeds, it sends the No. of start sector over UART
void M_Create_Swap_File(){
size = Mmc_Fat_Get_Swap_File(100);
if (size <> 0) {
UART1_Write(0xAA);
UART1_Write(Lo(size));
UART1_Write(Hi(size));
UART1_Write(Higher(size));
UART1_Write(Highest(size));
UART1_Write(0xAA);
}
}
|
For more detail: Connect Memory Card using PIC18F4520 Code