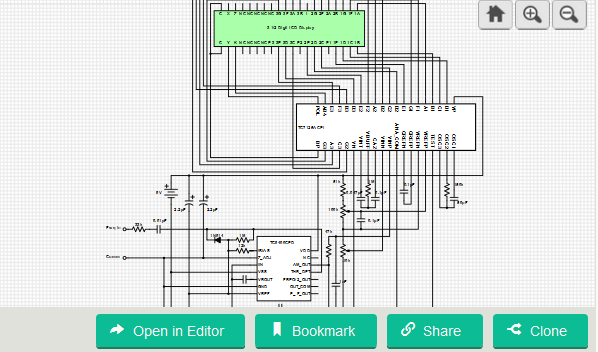
The circuit is a simple digital frequency meter that is made of a frequency-to-voltage converter and an analog-to-digital display converter that can be operated from a single 9-volt battery. The TC7126 ADC generates the voltage required by the TC9400 FVC with internal regulators. The TC7126 is designed to directly drive a 3-1/2 digit, non-multiplexed LCD display so no digital conversion is required.
The input circuit is made up of a current limiting resistor (33kΩ), a DC blocking capacitor (0.01µF), a clamping diode (1N914), and a biasing resistor (1MΩ). The diode acts as a soft clamp to prevent negative going transitions from latching the comparator input and the 33kΩ resistor limits the current during the positive transitions. The gain (VOUT vs. FREQIN) of the TC9400 is determined by the charge-balance capacitor and the integrator feedback resistor (620kΩ) that has been selected for an output of approximately +2V (referenced to ANALOG COMMON) with frequency input of 20kHz. The bias resistor (12kΩ) determined the input threshold of the comparator and has been selected for an input sensitivity range of 250mV to 10V peak-to-peak of a sine or square wave on the input of the FVC.
The TC7126 will have a maximum positive input of about 2V since the input is referenced to ANALOG COMMON that is only 3V below V+. The internal voltage swing of the integrator does not have the same limitation because a positive input results in a negative swing of the integration. A fully charged battery will give a range of about 6V. The integration components (1MΩ and 0.047µF) at pins VBUFF and VIN are selected, in conjunction with the oscillator frequency to have an integrator ramp amplitude of about –3V with a 2V input from the TC9400. The oscillator is set up to run at 48kHz (150kΩ and 50pF) for maximum rejection of stray power-line pickup. This will result in the TC7126 running at three conversions per second.
For more detail: Battery Powered Frequency Meter (0 to 20kHz)